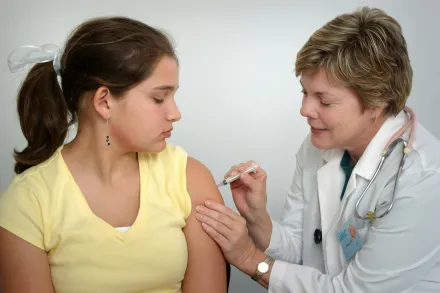
Vaccines stand at the intersection of science, medicine, and public health, embodying a disciplined approach to protect communities from disease. The development and testing of vaccines is a long and multifaceted process that blends curiosity about how the immune system works with methodical experimentation, careful observation, and strict oversight. Researchers begin with fundamental questions about how a pathogen interacts with the body, how immunity can be trained without causing disease, and what form of the immune response most effectively...
Medicine & Treatments
Deep vein thrombosis is a condition in which a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs, potentially causing pain, swelling, and, more dangerously, dangerous embolic events if a fragment breaks off and travels to the lungs. The condition arises from a combination of factors described by Virchow's triad: abnormal blood flow, injury to the vessel wall, and an excess tendency of blood to clot. In contemporary medicine, preventing DVT relies heavily on pharmacologic strategies aimed at reducing clot formation without causing excessive b...
Joint replacement surgery stands at the intersection of advanced engineering and clinical medicine, where damaged surfaces inside a joint are replaced with artificial components to restore smooth motion, reduce pain, and improve daily function. The procedure is typically considered after nonoperative treatments have failed to provide adequate relief or when the joint’s degeneration has progressed to a point that ordinary activities become increasingly difficult or painful. The goal is not merely to remove diseased tissue but to recreate a funct...
Fungal infections of the skin are among the most common health concerns encountered in daily life, touching people of all ages and backgrounds. These infections arise when microorganisms such as dermatophytes, yeasts, or non dermatophyte molds invade the superficial layers of the skin, keratinized tissues, and sometimes the nails. The typical presentation can range from red, scaly patches and itching to more subtle changes in texture and color, and in some cases the affected areas may become cracked or macerated due to prolonged moisture exposu...
Stroke remains a leading cause of disability and mortality worldwide. Ischemic strokes, caused by clot formation that blocks an artery in the brain, account for the majority of cases, while hemorrhagic strokes arise from bleeding into brain tissue. Anticoagulants are medicines that interfere with the blood coagulation system to reduce the formation of clots, particularly in conditions where clots are more likely to form inside the heart or large vessels. In the context of stroke prevention, anticoagulants are used to lower the incidence of card...
Vaccines are medical tools designed to prepare the immune system to recognize and neutralize pathogens without causing the illness themselves. They work by presenting the body with a safe version or part of a pathogen, or sometimes by delivering instructions that enable cells to manufacture that part. This early exposure triggers a cascade of immune events that lay the groundwork for rapid and specific defenses if the real microbe later tries to invade. The result is a memory friendly response that can prevent disease or lessen its severity, a ...
Chemotherapy stands as a central pillar in the treatment of pediatric leukemia, a disease that ranges from aggressive forms requiring rapid cytotoxic intervention to more subtle presentations that demand nuanced, risk adapted strategies. Over the decades, the careful orchestration of drug combinations, dosing regimens, and timing has transformed what was once a frequently fatal diagnosis into a condition with increasingly hopeful prospects for cure and long term survivorship. The focus here is to illuminate how chemotherapy functions within the...
Antipsychotic medications are a foundational tool in the treatment of serious mental illnesses that involve distorted thoughts, perceptions, and mood dysregulation. They have a long history that stretches back to the mid twentieth century, when the first-generation drugs opened new possibilities for reducing the intensity of psychotic experiences such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. Over time a diversity of compounds emerged, leading to a distinction between typical or first generation antipsychotics and atypical or sec...
Tapering pain medications is a deliberate and individualized process designed to reduce or stop a drug dose in a controlled manner. The goal is to minimize withdrawal symptoms, prevent a rebound of pain, reduce the risk of adverse effects, and support long term recovery or a safer transition to alternative therapies. In many cases, tapering arises when a patient has been on a medication for an extended period, when the drug is associated with growing side effects, or when a clinician determines that maintaining the same dose may not be medicall...
In medical care, pain is more than a symptom; it is a complex experience that colors how a patient perceives every other sensation and activity. Comfort, on the other hand, arises when distress from pain is minimized and basic needs are met, allowing the body to engage with healing processes rather than simply endure stress. The relationship between pain and comfort is intimate: when pain is poorly controlled, mobility, sleep, appetite, and mood often suffer, which in turn can hinder recovery. Conversely, effective pain management helps restore...